Deformable objects are ubiquitous in the world surrounding us, on all levels from micro to macro. The need to study such shapes and model their behavior arises in a wide spectrum of applications, ranging from medicine to security. In recent years, non-rigid shapes have attracted a growing interest, which has led to rapid development of the field, where state-of-the-art results from very different sciences – theoretical and numerical geometry, optimization, linear algebra, graph theory, machine learning and computer graphics, to mention a few – are applied to find solutions.
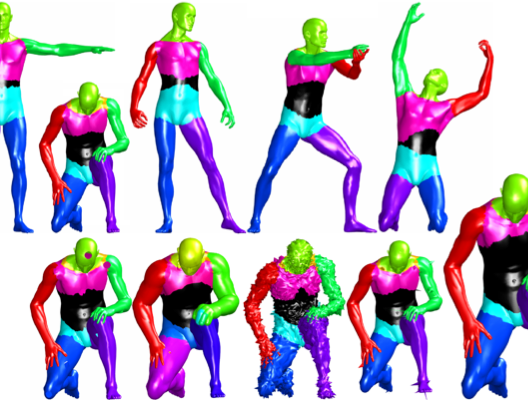

Maximally stable regions detected on shapes and different transformations
The purpose of the tutorial is to overview some state-of- the-art methods in the field of shape analysis through a consistent and rigorous mathematical framework.
The first part of the tutorial will focus on metric geometry approaches to shape analysis. Modeling shapes as metric spaces provides a common denominator for many problems in shape analysis. We will consider two archetype problems of similarity and correspondence.
Topics that will be covered include:
- metric model of similarity and correspondence
- invariance and isometry
- rigid isometry and iterative closest point methods
- multidimensional scaling and canonical forms
- fast marching
- Gromov-Hausdorff distances
- self-similarity, symmetry and structure
- correspondence and calculus of shapes
The second part of the tutorial will focus on diffusion geometry, arising from the geometric formulation of heat diffusion processes on manifolds. Diffusion geometry provides ways to construct robust global structures (metrics) and local structures (feature descriptors) for shape analysis.
Topics that will be covered include:
- diffusion and heat operator
- Laplace-Beltrami operator
- diffusion distances
- scale invariance and commute time distance
- spectral shape disances
- spectral symmetry
- heat kernel signatures
- bags of words
- volumetric diffusion